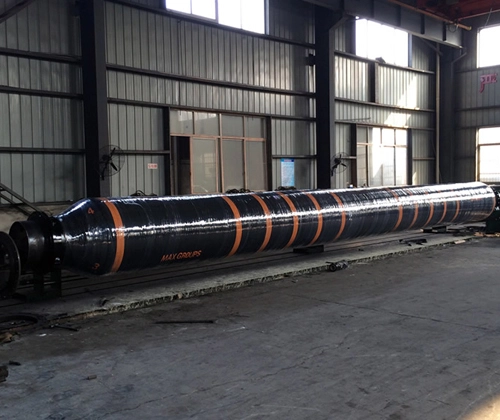
In port dredging, river regulation, land reclamation, and underwater pipeline laying projects, the transportation of sediment, water bodies, and solid-liquid mixtures is one of the core operational processes. To achieve efficient, safe, and adaptable transportation methods, engineering equipment relies on a specialized pipeline — the flexible dredge hose. This type of hose, with its excellent flexibility, wear resistance, and ability to adapt to complex environments, has become an essential piece of equipment in modern dredging projects. This article will provide a detailed yet accessible introduction to the definition, structure, and numerous advantages of flexible dredge hoses in practical applications.
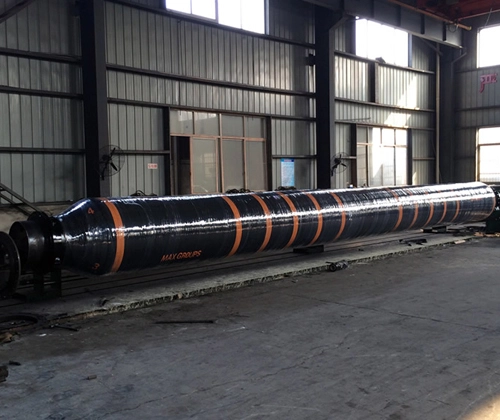

What is a Flexible Dredge Hose?
A flexible dredge hose is a high-strength rubber pipeline used for conveying mediums such as slurry, gravel, water bodies, and pebbles. It is usually used in conjunction with dredging ships, slurry pumps, and other equipment, installed between underwater, deck, or floating structures. Its most notable feature is its softness and elasticity, which allows it to withstand pipe bending, pressure impacts, and frequent movements, adapting to various complex working conditions. For example, a self floating rubber hose is specifically designed for these applications, ensuring efficient operation in diverse environments.
The basic structure of a flexible dredge hose includes:
Inner Rubber Layer: Directly contacts the conveying medium, offering high wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
Reinforcement Layer: Composed of multiple layers of high-strength cord, steel wire, or synthetic fibers, providing pressure and tensile support.
Outer Rubber Layer: UV-resistant, anti-aging, and seawater-resistant, protecting the overall structure of the hose.
Flange Joint: Facilitates connection with steel pipes, pumps, and other equipment, ensuring continuity in transportation.
Main Advantages of Flexible Dredge Hoses
Excellent Flexibility to Adapt to Complex Terrains
The core advantage of flexible dredge hoses is their high flexibility. In irregular terrains such as seabeds and riverbeds, rigid steel pipes often cannot be smoothly laid or flexibly adjusted with environmental changes. In contrast, hoses can easily handle various winding paths, ensuring the integrity and smoothness of transportation pipelines.
This flexibility also allows the hose to automatically adjust its position during operations, following vessel movements and wave fluctuations, greatly reducing the risk of leakage or breakage at connection points. The armor flex hose is particularly known for this adaptability.
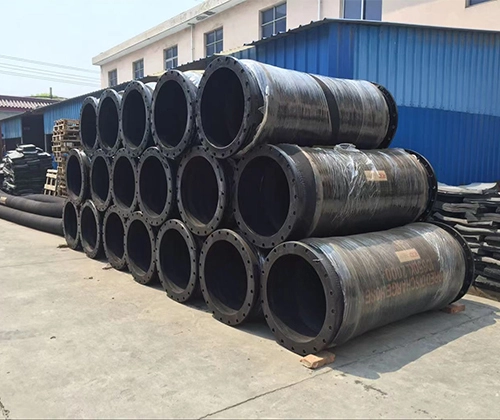

Superior Wear Resistance and Long Lifespan
Dredging mediums often contain a large number of hard particles, such as gravel, shells, and clods, which cause severe wear on the inner wall of pipelines. The inner layer of flexible dredge hoses, typically made from natural rubber or highly wear-resistant synthetic rubber, can significantly extend the service life of the pipeline, reduce replacement frequency, and lower maintenance costs. This makes them a preferred choice among dredge rubber hose manufacturers.
Easy Installation and Low Maintenance Costs
Compared to heavy, rigid metal pipelines, flexible hoses are lighter, easier to transport, and can be quickly deployed on the water surface, underwater, or on the deck, saving a lot of labor and mechanical costs. Their flanged connection design also makes maintenance more convenient, allowing partial replacement or disassembly without complex equipment.
Additionally, flexible dredge hoses have strong fatigue resistance, making them less prone to damage from repeated bending, greatly reducing the risk of downtime for repairs. The role of sealing element suppliers is crucial in ensuring these connections remain leak-free.
Good Weather Resistance and Adaptability
Whether in high-salt, high-humidity marine environments or hot and humid tropical regions, flexible dredge hoses can maintain stable performance over long periods. The outer rubber material features excellent resistance to UV rays, ozone, and seawater corrosion. Even when used under exposed conditions for several years, they will not crack or age.
Supports Various Transportation Needs
Flexible dredge hoses can be customized with different diameters, lengths, pressure ratings, and inner lining materials to meet various medium transportation needs, from soft mud to coarse sand, and from water slurry to rock chips. They can also be configured with floating layers, underwater reinforcement layers, or vacuum support layers according to the application scenario, making them suitable for special applications such as deep-sea, high-pressure, or floating platform operations.
- What Makes a High-Quality Dredging Rubber Hose?
- The Unique Advantages of Floating Dredging Hoses
- Sewer Seal Ring: Securing Urban Infrastructure
- Marine Fender Suppliers: The Invisible Guardians of Port Safety
- Flexibility and Customization: The Core Competitiveness of Dredge Rubber Hoses
- Comparison of Floating Rubber Hose with Other Types of Hoses
 English
English