In the world of dredging, two primary techniques stand out: hydraulic and mechanical dredging. These processes are crucial for maintaining navigable waterways, constructing ports, and executing maintenance dredging projects. Each method has unique advantages and applications, playing different roles depending on the project's specific needs. This article explores the differences between hydraulic and mechanical dredging, analyzing their efficiency, costs, environmental impacts, and the scenarios where each is most applicable. Whether dealing with dredge pipe suppliers or ship sealing requirements, understanding these dredging techniques can maximize project success and sustainability.

Method Differences
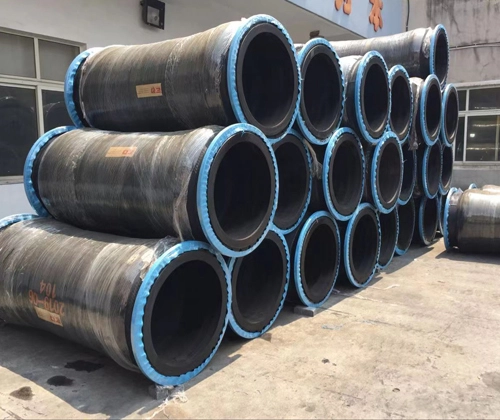
Understanding the fundamental differences between hydraulic and mechanical dredging is essential for selecting the appropriate method. Hydraulic dredging involves the use of pumps and suction equipment to remove sediments and transport them through a flexible rubber hose or self floating dredge hose. This method is ideal for handling fine materials and is often used in maintenance dredging of shallow waterways.
In contrast, mechanical dredging employs heavy machinery like clamshells, backhoes, or bucket dredges to excavate material directly. This method is suitable for projects involving coarse materials or when precise excavation is required. The choice between sealing element suppliers and marine fender suppliers is also crucial for structural integrity and operational success.
| Dredging Method | Equipment Used | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Hydraulic Dredging | Pumps, Suction pipes | Fine materials, large-scale sediment removal |
| Mechanical Dredging | Clamshells, Backhoes | Coarse, heavy materials |
Efficiency Comparison
Efficiency in dredging is determined by material type, site conditions, and environmental considerations. Hydraulic dredging is generally more efficient for projects requiring the movement of large volumes of finer sediment over long distances. The use of discharge hose systems and mud suction hose with rubber pipe fittings allows for flexibility and smooth transport of dredged materials.
On the other hand, mechanical dredging offers efficiency in projects where precise excavation is critical. For example, when dealing with large boat fenders or installing dock fenders, the precision of mechanical dredging is unparalleled. The attachment of self floating rubber hose connectors in these setups ensures a secure and functional structure.
Cost Analysis
The cost of dredging projects can vary significantly depending on the method employed, with factors like equipment, labor, and environmental protections influencing expenses. Hydraulic dredging generally incurs lower transportation costs compared to mechanical dredging due to rubber expansion joints and continuous operation capabilities.
Mechanical dredging may involve higher upfront equipment costs and is often labor-intensive. However, the cost-effectiveness shines in scenarios needing robust handling of heavy or compact materials. For projects requiring the durability of industrial rubber and gasket components, the investment in mechanical dredging equipment pays off in performance reliability.
Environmental Impact
Environmental considerations are critical when selecting a dredging method, as each has distinct impacts on surrounding ecosystems. Hydraulic dredging, due to its fluid transport systems, can minimize disturbances to benthic environments when using inside marina fenders for controlled operations.
Nevertheless, mechanical dredging often results in more significant habitat disruption due to direct excavation but can be mitigated through strategic timing and the use of marine sealing technologies. Project planners should weigh these impacts carefully, considering local regulations and ecosystem sensitivity.
Best Scenarios
Choosing between hydraulic and mechanical dredging depends on project-specific needs. Hydraulic dredging excels in environments requiring large-volume sediment handling, especially where transport over long distances using flexible dredging hose is advantageous, such as in river dredging or removing soft sediment layers.
Conversely, mechanical dredging is the preferred choice for projects demanding precise excavation and material handling, such as harbor construction or projects involving big boat fenders installation. Its ability to tackle dense substrates efficiently makes it suitable for challenging dredging scenarios.
By considering factors like the presence of rubber for boat applications and the size of fenders for boats, operators can optimize dredging strategies for both effectiveness and environmental responsibility.
Conclusion
In summary, both hydraulic and mechanical dredging play critical roles in maintaining and developing water-based infrastructures. Understanding their differences in method, efficiency, cost, and environmental impact is crucial for selecting the right approach for a given project. Projects involving rubber gasket and marine fende technologies benefit from the specificity these dredging methods provide.
Ultimately, the choice between hydraulic and mechanical dredging should be guided by project goals, available resources, and environmental considerations. Whether maintaining existing waterways or initiating new construction projects, these dredging methods ensure that water-based operations continue smoothly and sustainably.
Don't Miss These Blogs
floating dredging hose market analysis report
- Optimizing Channel Maintenance Dredging with Advanced Rubber Dredge Hose Solutions
- Marine Rubber Seals: Key Components for Ensuring the Safe Operation of Ships and Offshore Equipment
- Installation Process of Marine Rubber Fender
- Understanding Materials, Length, and Applications for Optimal Dredging Performance
- Dredging Hose Selection Questionnaire
- Case Study: Small Dredging Project at a Local Marina
 English
English